VENUE
The 9th International Symposium “Systems with Fast Ionic
Transport” will be organized in capital of Latvia Riga. Symposium will take
place at the Main Building of the University of Latvia at the City centre -
Raina boulevard 19, Riga.
Some facts about Latvia
1.
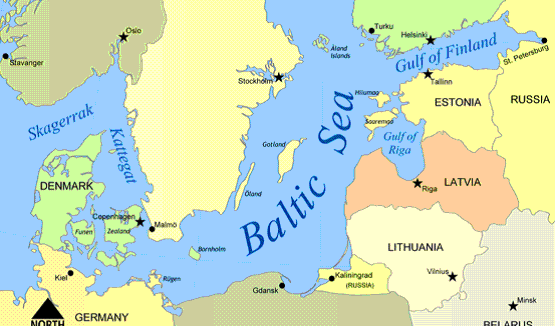
LATVIA: IN BRIEF
Latvia
is situated on the shore of the
Baltic Sea, sharing borders with
Lithuania
to the South,
Estonia
to the North,
Russia
to the East and
Belarus
to the South East.
Territory and
population
The area of
Latvia
is about 64 thousand square kilometres. The population of the Republic is 2.3
million people, of which 59% Latvians, 28% Russians, 4% Byelorussians, as well
as Ukrainians, Poles, Lithuanians, Jews and other nations.
The biggest
cities are:
Riga
(722 thousand inhabitants),
Daugavpils
(108 thousand inhabitants),
Liepaja
(85 thousand inhabitants), Jelgava (66 thousand inhabitants), Jurmala (55
thousand inhabitants) and Ventspils (43 thousand inhabitants).
Latvia
is divided into four historical areas: Vidzeme, Kurzeme,
Latgale and Zemgale. The highest peak is Gaizinsh standing at 311.5 meters. The
climate in
Latvia
is moderate with some temperature fluctuation. The summer is warm, the weather
in autumn and spring is relatively mild but the unstable winters sometimes
getting really cold.
Languages
The official
language is Latvian. Russian language is often spoken, English and German not
too common but in use.
Religion
Latvia
has no official religion, but most population is Lutheran,
Catholicism prevails in the East. The Orthodox and Old Believer communes in
Latvia
are rather large. In general the society is tolerant to different religions,
however the church does influence the mood of society.
State symbols
The Latvian
flag is very similar to the Austrian flag, but darker in colour. It is made of
bands of dark red, white, and dark red (from top to bottom). The white band is
narrower than the red ones. The national anthem “Dievs, svēti Latviju!”
(God, bless
Latvia
!) was written by a Latvian Composer Karlis Baumanis in the second half of the
19th century and became the national anthem in 1918. The Latvian Coat of Arms
– a shield with a rising sun on the blue background at the top; the red lion
on the silver background to the left and the silver griffin on the red
background to the right.
State
political system
Latvia
is a Democratic Republic. The Prime Minister is appointed by
the President of the Republic and is the head of the government. The President
of Latvia is elected by the Parliament and runs a four year term. The President
is mostly representative authority, however he can block some decisions of the
parliament.
International
relations
After the
restoration of independence in September 1991
Latvia
headed towards joining European and international organizations, since April
2004
Latvia
is a member of NATO and since May 2004 – a member of the European Union.
Latvia
is a member of WTO.
2. LATVIAN
HISTORY
Latvian
history can be divided into two periods:
1. Before the
national republic was founded (in 1918)
The first
state formations on the territory of modern
Latvia
were founded in the XIII century by German knights. In the 16th-17th centuries
Latvia
was ruled by Polish-Lithuanian princedom and
Sweden
and in the beginning of the 18th century – by Russian Empire. World War I and
the revolution in
Russia
create the necessary prerequisites for the foundation of an independent Latvian
state.
2. Latvian
history in the XX century
The
independent Latvian republic was proclaimed on
November 18, 1918
. In 1940
Latvia
loses independence end joins the
USSR
. The Gorbachov’s Perestroika and the breakdown of the
Soviet Union
lead to restoration of the independent
Latvia
Republic
in on
August 21, 1991
.
3.
AIR
TRAVEL
For arranging
your flights to/ from Riga, we suggest to use the following information sources:
You can find
flight schedules as well as book flights online at www.airbaltic.com
Other major
European air company operating flights to/ from
Riga:
Riga
International airport site at www.riga-airport.com
provides list of all airlines
operating flights to/ from Riga.
4. MONEY,
TRANSPORT, COMMUNICATION IN LATVIA
Time
Latvia
is in the −
GMT
+2 time zone. If you arrive from London, put the clock back for two hours, from
Moscow
– forward one hour. For precise time call 154 (in Latvian) or 174 (in
Russian).
It is quite
hard to find a 24/7 store in Riga. The supermarkets usually open at
8 AM
and close at
11-12 PM
. On Saturdays and Sundays grocery stores are usually open but the others are
either closed or close earlier. Banks and museums close at
4-5 PM. Most large cafes are open until
11 PM
−
1 AM
. Most service enterprises work without a lunch break.
Money and payment cards in
Latvia
The currency
in Latvia
is Lat (Ls), one Lat is equal to 100 santims. The Lat exchange rate is stable.
One Lat is equal to app. 1.4 Euro or 2 Dollars. There are 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 and
500 Lat notes and 1 and 2 Lat and 1,2,5,10,20 and 50 santim coins. Currency
exchange has a billboard “Valutas maina”. There are no legal limitations of
currency transfer across the borders of
Latvia
. You do not have to show your passport to change currency.
There is no
problem with getting cash from your payment cards as there is a broad bank
machine network that lets you get Lats in almost any town of
Latvia. Except offices, banks and central streets there are bank machines in large
shopping centers and fuel-tanks. Most stores, hotels, restaurants accept debt
and credit cards.
Before
departure ask the bank that issued your card about fees for cashing it and
paying for goods. You can cash also in Travel cheques American Express &
Thomas Cook in bank offices.
Telephone
Latvian
telephone connection is almost totally digital and for that reason of very high
quality. Connection is fast and easy and audibility is usually very good. You
can call any place in the world from phone booths located all around Latvia. You can use a 2, 3 and 5 Ls call card, sold in all press boots, or with a
credit card. Phone-calls in Latvia
are quite expensive. There are instructions in every phone booth. You should
remember that a call to
Europe
or USA
costs less than a call to Russia
or CIS countries. To call a foreign number you should dial 00 and then (don’t
wait for the beep) the code of the country you are calling and the telephone
number.
Mobile
communication
Mobile
connection in Latvia is very well developed. Almost all territory
of
Latvia
has cell coverage. Pay attention to the fact, that mobile phone users do not
have to pay for incoming calls and a call from a stationary phone to a mobile
phone usually costs much more, so you will save by calling a mobile phone from
another mobile phone.
Tourists are
recommended to buy pre-payment cards – “O karte”, "BiFri" or “Zelta Zivtina”
that provide you with a temporary number and call opportunity for local prices.
Mail
Mail in
Latvia
works well. Letters are usually delivered on the next day (across
Riga
) and in one-two days across
Latvia
. International letters are usually delivered in under a week. To send a letter
you have to buy post stamps in post offices or Narvessen shops and stick them on
envelopes. Across
Latvia
– 35 santims, European counties and
Russia
– 55 santims, to other countries – 60 santims.
Transport
Riga
has no subway but there are trams, trolleybuses, buses and
route taxis. Public transport fee is 50 santims, taxi-buses – 50-70 santims.
You pay the conductor as you enter except trams, where you can buy ticket from
the driver for 70 santims or need to buy tickets beforehand at any press boot.
There is very little transport after 11 PM. Some routes have duty buses and trams (once in an hour).
• You can
find the list of tram trolleybus and bus routes and their timetables at
www.rigassatiksme.lv (the information is available in Russian, English).
• Local
train timetable at Latvian railroad web-site (Russian and English available).
• Local
Latvian bus timetable at Riga Autoterminal web-site
Taxi
There is no problem with finding a taxi
in Riga. Day fee (
06:00 – 24:00
) is approx. 1.00-1.50 Ls for entry and 0.40-0.50 Ls p/km. Night fee is more
expensive.
Taxis are available at taxi stops and
via phone. A ride across the city will cost you 5-8 Ls. You have to count
traffic jams in Riga, especially during rush hours (7.00-10.00 and 16.00-19.00), which will increase
the travel time and the fee.
We don’t usually stop private cars in Latvia. Hitchhiking is not generally in style.
Information services
Main information telephone number is
1188 − paid service. A call costs app. 10 santims + the time of your
conversation with the operator on a standard tariff. Service quality is very
high, operators are able to answer even the most unexpected questions. Operators
speak Latvian, Russian and English.
To find companies and enterprises in Latvia, we recommend online data-base www.zl.lv,
or www.1188.lv Latvian
commercial data base, where you can find juridical data and official financial
report data on a concrete company is available at www.lursoft.lv
but is mostly on a paid basis.
5.
MAP OF RIGA
6. OTHER
USEFUL LINKS IN LATVIA
In order to find more about Riga
and Latvia, please, check the following links:
Information about Latvia
and its people –
Latvia
in brief, symbols, nature, history, society, culture, economy: www.li.lv
Riga
In Your Pocket Guide – arrival, hotels, local essential
information: www.inyourpocket.com/latvia/riga/en/
Virtual Riga
– hotels, map, travel info: www.virtualriga.com
Interactive Maps of Latvia
– institutions, leisure, shopping, transport, services: www.uzkartes.lv
Currency exchange rates – The Bank of
Latvia, financial information, exchange rates: www.bank.lv
Weather online Riga
and Latvia
www.weatheronline.co.uk/Latvia.htm;
www.meteo.lv
Information about the city of Riga
For more information about Riga see:
http://www.riga.lv/
University of Latvia
For more information about University of Latvia see: http://www.lu.lv

